
There are at least a dozen or more different sets of reference temperature and pressure that are referred to as standard or normal. There is no universally accepted Standard Temperature and Pressure or Normal Temperature and Pressure for gases. Just think of STP or NTP as being another way of expressing mass. The only reason is to make flow rates under widely differing conditions comparable.Ĭonverting to standard temperature and pressure or normal conditions is just a way of converting volumetric quantities Gas volume is directly proportional to temperature and inversely proportional to pressure.īelow are different examples of calculation of molar volume of any ideal gas in several standard temperature and pressure reference conditions: In SI metric units: Vm = 8.314472 x 273.15 / 101.325 = 22.414 m3/kmol at 0 ☌ and 101.325 kPa absolute pressure Vm = 8.314472 x 273.15 / 100.000 = 22.711 m3/kmol at 0 ☌ and 100 kPa absolute pressure In customary USA units: Vm = 10.7316 x 491.68 / 14.696 = 359.0441 ft3/lb-mol at 32 ☏ and 14.696 psia Vm = 10.7316 x 491.68 / 14.730 = 358.2154 ft3/lb-mol at 32 ☏ and 14.73 psia R = the universal gas law constant of 10.7316 ft3.T = the gas absolute temperature, in degrees Rankine (°R).V = the gas molar volume, in ft3/lb-mol.R = the universal gas law constant of 8.314472 m3.The molar gas volumes can be calculated with an accuracy that is usually sufficient by using the ideal gas law: To convert from Normal or Standard Conditions to Actual (Operating) Conditions the molar gas volume is needed.

Usually, Normal Volume is considered as a unit of mass for gases equal to the mass of the reference volume measuredĪt a pressure and temperature of reference conditions.įor example, Ndm3 is a unit of mass for gases equal to the mass of 1 liter (0.035 3147 ft3) at a pressure of 1 atmosphereĪnd at a standard temperature, often 0 ☌ (32 ☏) or 20 ☌ (68 ☏).
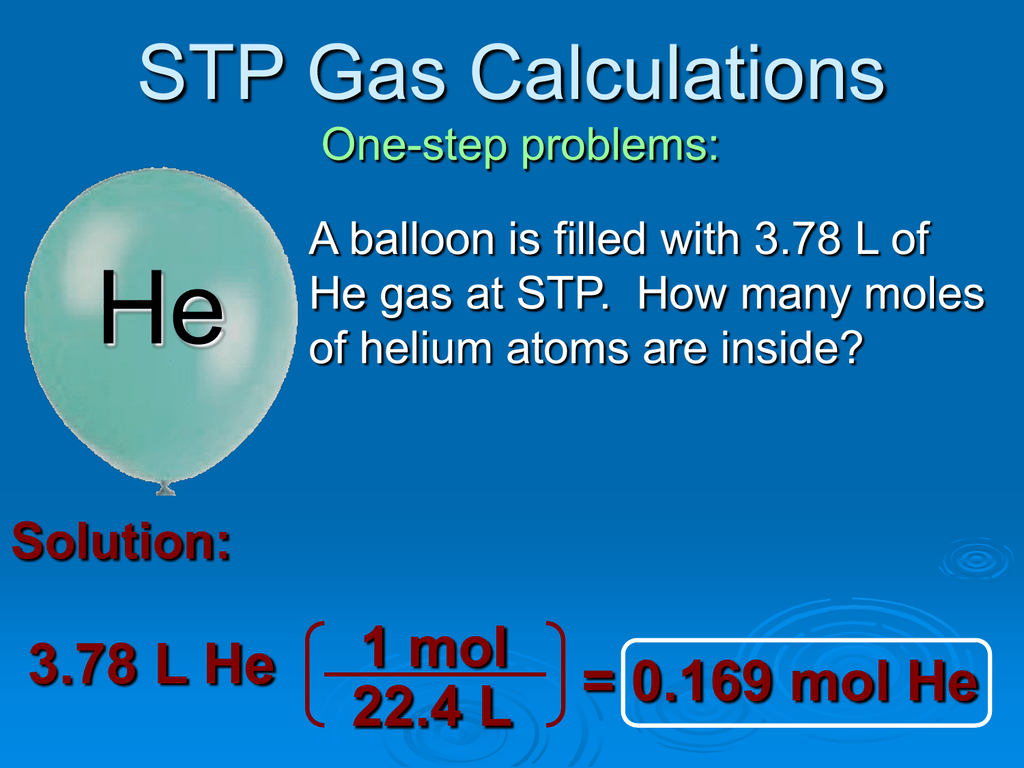
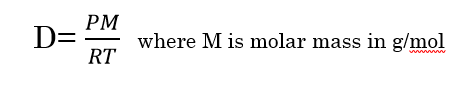
So it is more concise to discuss these systems in terms of mass or standard volume flow. Unless there is a leak, the mass / standard volume flow stays the same, This makes the specification of volume flow particularly prone to error and misinterpretation. Which means the actual volume flow is changing. In systems with vacuum pumps, blowers, compressors, and heat exchangers, air pressure and temperature are constantly changing, Mass flow rate = density* Volumetric flow rate. Stating an air flow in units of SCFM makes it easy to compare conditions, and certain calculations simpler. Since the air density of an air flow stated at standard conditions (SCFM) is always the same, it is essentially a mass flow rate! If we take Air for example, Air density at standard conditions is. In general, the standard pressure is close to atmospheric pressure and the standard temperature is close to the ambient temperature value. These standards depend on the organization that defines them. There are different standards that define different temperature and pressure values. Once the volume is calculated, we can convert the calculated amount into an amount of moles or mass of gas. Therefore, we can use the reference temperature and pressure conditions to specify the volume of gas measured under those conditions. It is necessary to define the corresponding temperature and pressure conditions for the volume measurement. The reason is very simple, the volume of a constant number of moles of gas depends on the measurements of temperature and pressure.ĭue to this reason, whenever the quantity of gas is specified in terms of gas volume,
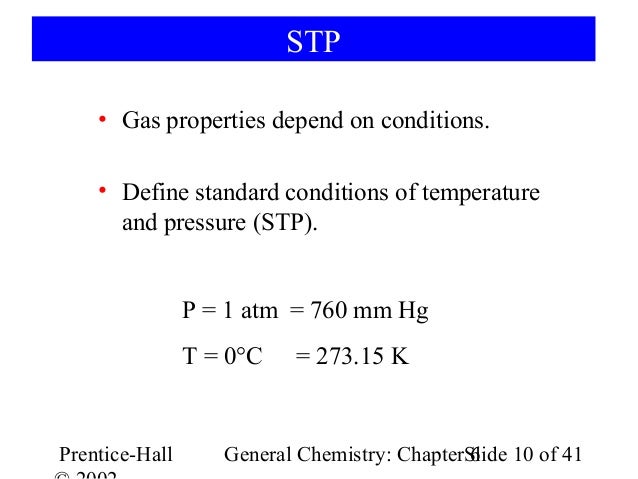
Normal or Standard temperature and pressure conditions are generally used. Standard or normal conditions are used as reference values in thermodynamics of gases.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
